We covered the basics of electric vehicles (EVs) as well as the different types of EVs in the Indian market in our previous posts. As you must know by now, an important aspect of owning or operating an EV is the way it is charged. This further relies on the type of charger you use to juice up your EV. In this article, we shall go through these types of EV chargers prevalent in India, as well as some great practices you should follow to charge your EV in the best manner possible.
Before we dive deeper into the types of EV chargers available in the market, it is important to know some of the terminology associated with EV charging. As things stand, certain confusion around EV chargers arises due to differences in the types of EV chargers used across different regions of the world. So first, let us get our basics straight.
The most common distinction between EV chargers is made using the term “Level.” Another is based on the “Types” of EV charger plugs available in the market. Both these terms usually indicate one thing – the power output you can expect out of an EV charger.
Other terms associated with EV charging include –
- Charging outlet – The electric plug on the home/ public charging station through which you will charge your EV.
- Charger – The piece of equipment that is plugged into the outlet and to your EV’s port, in its entirety, is called an EV charger.
- Charging plug – The head of the charger that plugs into the EV port.
- Charging port – The portion in your car where the EV charger is plugged.
Now that we know this, here is a look at the different types of EV charging stations.
- Level 1 Charging Station: Level 1 chargers are the slowest type of charger, providing a charging rate of approximately 7 to 8 km of range per hour. They are typically used with a standard 120-volt household outlet and are the most affordable option. Level 1 chargers are best suited for those who have a short commute and usually charge their EV overnight at home.
- Level 2 Charging Station: Level 2 chargers are the most common type of chargers found in public EV charging stations like those in a mall or an office complex. These provide a charging rate of approximately 40 km of range per hour. They require a 240-volt outlet, similar to those used for large appliances such as a washing machine. Level 2 chargers are ideal for those who need to charge their EV at home or at work, and can fully charge an EV in about 4 to 8 hours.
- Level 3 or DC Fast Charging Station: DC fast chargers are the fastest of the lot and provide a charging rate of approximately 250 to 400 km of range per hour. They can often juice up an EV completely in about an hour.
These chargers use direct current (DC) to charge the battery, rather than alternating current (AC), which is used by Level 1 and Level 2 chargers. DC fast chargers are typically found at public charging stations on the highways.
As mentioned, these three different “Levels” indicate the total output you can expect out of the EV charging setup. Yet another distinction can be made on the basis of the plugs that these EV chargers use.
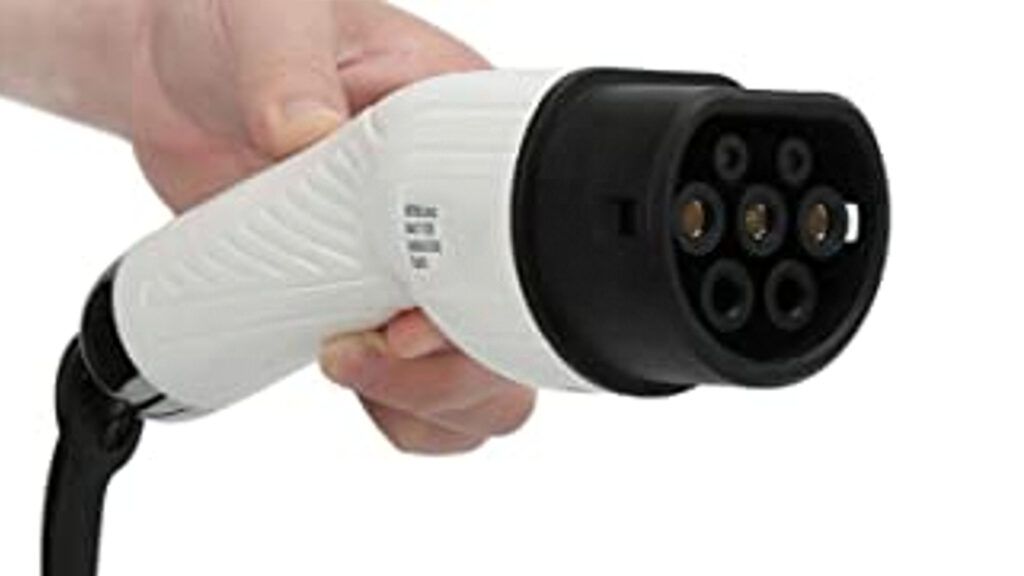
- Type 1 charger: Also known as a “J-Plug charger,” this type of charger uses a J1772 connector to plug into the vehicle. These are typically used in North America for both Level 1 and Level 2 charging and can be identified through their 5-pin design.
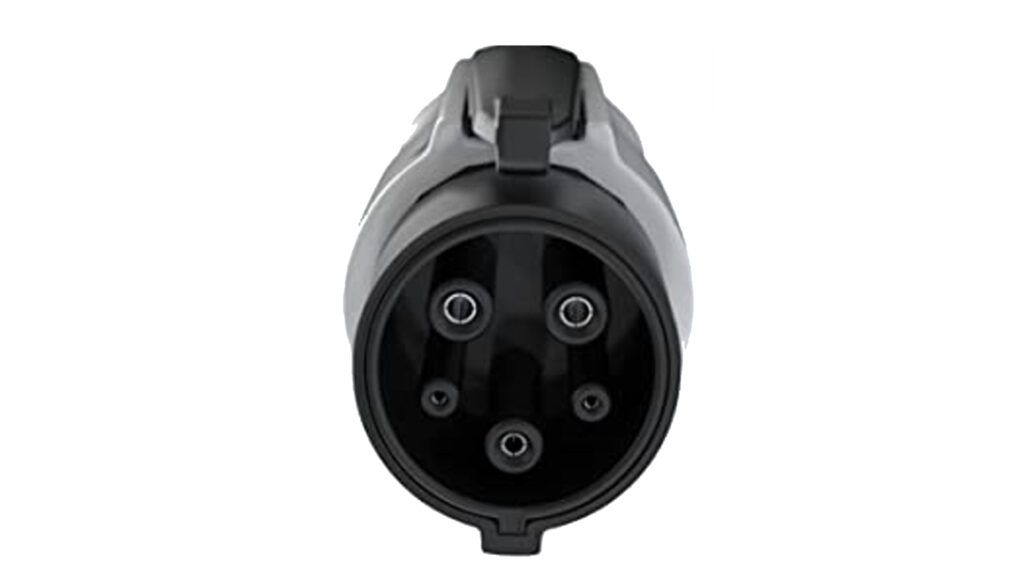

- Type 2 charger: The European alternative of J-Plug chargers, these types of chargers come with a 7-pin design and allow for a faster flow of electricity, meaning faster charging for EVs. These are more commonly used across the world as compared to the J-Plug chargers and are also the standard home EV chargers in India.

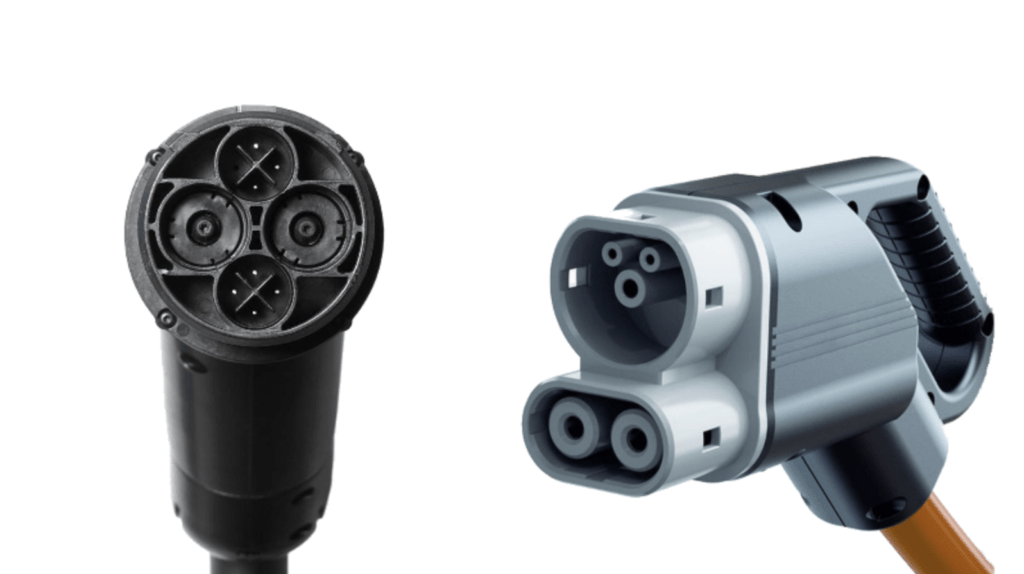
- Type 3 chargers: A total of 3 options are available when it comes to Level 3 charging. Though in India, we may need to concentrate on just one, and that is the Combined Charging System or CCS.
- CCS chargers are the same as the J-Plug charger plugs but with two additional high-speed charging pins below them. This is also where the name “Combined Charging System” comes from. As these were developed by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), these are also known as SAE DC chargers.
- CHAdeMO chargers are developed and used by Japanese automakers such as Nissan and Mitsubishi which is a completely different plug type for DC charging. However, their use is slowly coming to an end as CCS chargers take over.
- Tesla has a patented charging system that uses a unique plug type at its DC charging stations, also known as Tesla Superchargers.

Now that we know the different charger types, here are some tips to keep in mind while charging your EV.
- Start charging your EV’s battery before it is completely empty.
- Charge to 80 percent to extend battery life. This is also the point where fast charging stops and trickle charging starts.
- Avoid frequent fast charging as it can degrade the battery.
- Use the appropriate charger for your EV to ensure compatibility.
- Only use home chargers as recommended by your EV maker.
As charging your EV is a repeated practice, you should make sure to use the best ways to juice up your EV for its long life. We hope these distinctions in the charger types and the associated tips with their use should help you choose the right options for charging your EV every time. In case you have any questions, feel free to leave it in the comment section below and we shall make sure to reach out to you soon.