Renault-Nissan has cancelled plans for a low-cost EV for India, reports Autocar India. The alliance aims to develop an electric SUV comparable to the Creta, based on the CMF-B EV platform.
Last year, Nissan Motor Corporation and Renault SA restructured their global alliance, allocating Rs 5,300 crore for six models in India, including two EVs.
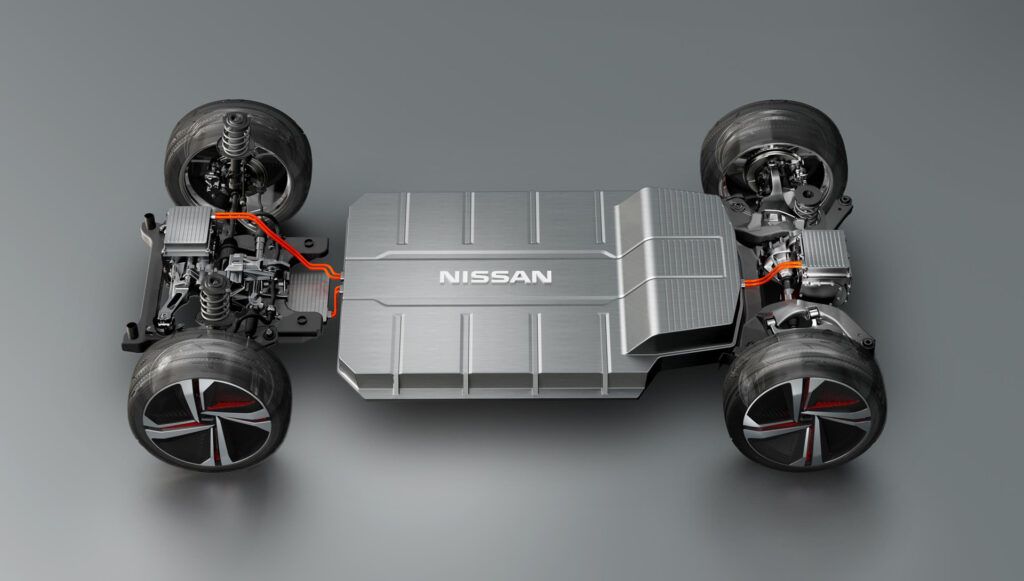
Based on a global plan, Nissan aims to launch 30 new models over the next three years, including 16 EVs and 14 ICE vehicles.
On the other hand, Renault achieved a milestone by producing 1 million vehicles in India last year. Now, it aims to double to 2 million by 2030 through new launches and a planned entry into the EV market.

Shift to C-Segment EV Strategy
According to sources, the alliance deemed the entry-level EV proposed for the Indian market last year unviable.
Furthermore, the companies are now considering a C-segment EV with a length exceeding 4 meters. Priced between Rs 15 lakh and Rs 20 lakh, it aims to compete with Maruti Suzuki’s eVX and Hyundai Creta EV.
Also, Autocar India’s sources reveal that the Renault-Nissan alliance has initiated talks with local cell and battery manufacturers for affordability. With an LFP battery, the vehicle may achieve a range of 300km per charge, according to reports.
Further, the Renault Nissan Technology Business Centre India will rely heavily on localization and indigenous development efforts.
While facing minor setbacks, the global rollout of the CMF-B EV platform is reportedly underway. Additionally, the company has scheduled to prepare it for market release between 2026 and 2027.

EV Localization, Adoption, and Compliance
The upcoming EVs must achieve at least 70% localization and implement a robust export strategy for a sustainable business model.
Again, the adoption rate of electric vehicles in India is still significantly low compared to conventional cars.
Nevertheless, strategically integrating a battery electric vehicle (BEV) is crucial for achieving future CAFÉ compliance for a country. In the absence of such measures, noted one of the sources, the alliance partners could face considerable penalties.
But, when contacted for a statement, a spokesperson from Renault and Nissan Motor India declined to comment on speculation.