Gotion High-tech, a Chinese battery cell manufacturer, has unveiled an electric vehicle battery that charges in under 10 minutes. This positions the company as a competitor to CATL, the global leader in the industry.
During a tech conference at its Hefei headquarters, Gotion revealed the G-Current battery. It showcased its ability to charge from 10% to 80% in 9 minutes and 48 seconds.

About Gotion’s New Battery
Gotion, backed by Volkswagen, engineered the G-Current using a fresh combination of materials. The company claims an enhanced conductivity of the lithium-ion electrolytes by 30% to 50%.
The battery pack has a thinner profile and 30% fewer components, allowing installation in electric vehicles from coupes to SUVs.
The G-Current will be available in two variants. The lithium iron phosphate (LFP) type excludes rare metals and is cost-effective. Meanwhile, the nickel-manganese-cobalt version, more conventional, offers extended driving ranges.
Gotion has initiated the mass production of G-Current batteries designed specifically for extended-range EVs, which belong to the hybrid category.
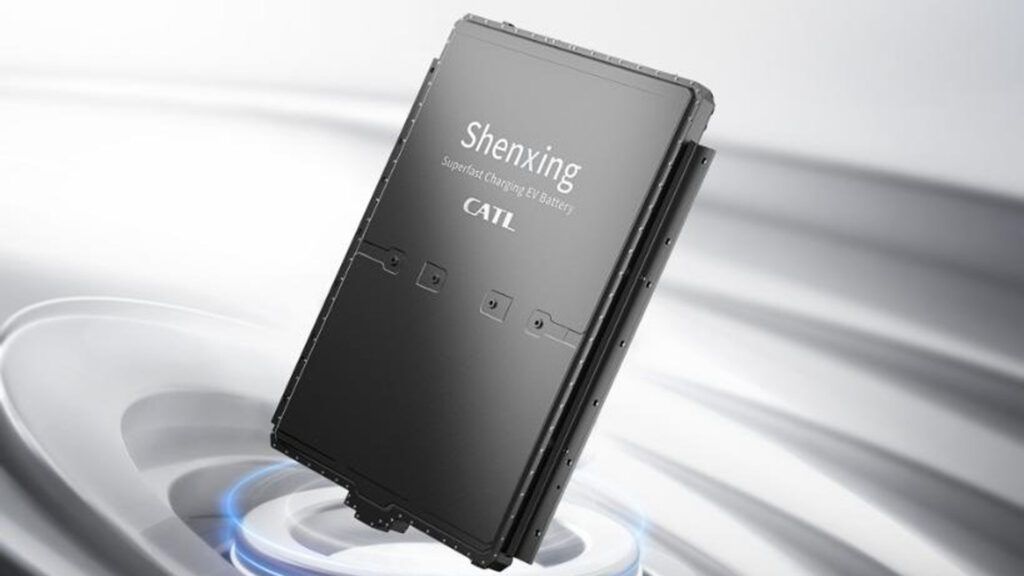

CATL Shenxing Batteries: Fast, Efficient, Long-Range
As per statistics from the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers, new energy vehicles make up 32% of total new car sales in China, including exports. Among these, electric vehicles (EVs) constitute 20% of the overall sales volume.
The adoption of new energy vehicles has become widespread, with queues forming at charging stations being a frequent occurrence.
To tackle this issue, manufacturers have been working on reducing charging durations. Previously, EV platforms were designed for use with 400-volt chargers. However, now, there is a race among developers to introduce batteries compatible with 800-volt chargers.
CATL, the world’s top EV battery manufacturer, introduced the Shenxing Plus battery at the Beijing auto show in April. According to CATL, this latest LFP battery offers a range of 600 km after just a 10-minute charge and can travel up to 1,000km on a full charge.
CATL also manufactures the Shenxing superfast charging battery. Electric vehicles manufactured by Zhejiang Geely Holding Group under the Zeekr brand and Chery Automobile’s Exeed series utilize the Shenxing batteries.

Adoption of 800-V Charging Technology
European and South Korean car manufacturers have made significant progress in high-voltage charging technology. In 2019, Porsche introduced the Taycan electric vehicle, capable of charging at 800 volts. According to the German automaker, the 2024 model, equipped with batteries sourced from South Korea’s LG group, can charge from 10% to 80% capacity in 18 minutes.
Hyundai Motor launched the Ioniq 5, which supports 800-volt charging. As a result, Chinese electric vehicle manufacturers are now adopting similar technology with expectations of a surge in new energy vehicles compatible with 800-volt charging in the Chinese market.
According to Soochow Securities, a Chinese brokerage firm, 125,000 new energy vehicles using 800-volt platforms were sold in China last year. They anticipate this number to surge to approximately 1.32 million units by 2025.
The projected global market for such vehicles in 2025 is 1.62 million units, with China expected to be the primary driver of the market for electric vehicles with superfast charging capabilities.
LFP batteries can make EVs more affordable for the masses. Gotion plans to integrate its latest line of batteries into midsize models of new energy vehicles, representing more than 30% of the market.
One of the primary challenges is the expansion of charging station networks to accommodate EVs equipped with 800-volt charging technology. This is necessary to support the growing adoption of electric vehicles equipped with advanced charging capabilities.